MobiCom ’18 Demo Accepted
Our demo paper Linux Goes Apple Picking: Cross-Platform Ad hoc Communication with Apple Wireless Direct Link was accepted at ACM MobiCom ’18. In the demo, we present a working prototype of AWDL for Linux-based systems. Read our paper here.
Abstract
Apple Wireless Direct Link (AWDL) is a proprietary and undocumented wireless ad hoc protocol that Apple introduced around 2014 and which is the base for applications such as AirDrop and AirPlay. We have reverse engineered the protocol and explain its frame format and operation in our MobiCom ‘18 paper “One Billion Apples’ Secret Sauce: Recipe of the Apple Wireless Direct Link Ad hoc Protocol.” AWDL builds on the IEEE 802.11 standard and implements election, synchronization, and channel hopping mechanisms on top of it. Furthermore, AWDL features an IPv6-based data path which enables direct communication. To validate our own work, we implement a working prototype of AWDL on Linux-based systems. Our implementation is written in C, runs in userspace, and makes use of Linux’s Netlink API for interactions with the system’s networking stack and the pcap library for frame injection and reception. In our demonstrator, we show how our Linux system synchronizes to an existing AWDL cluster or takes over the master role itself. Furthermore, it can receive data frames from and send them to a MacBook or iPhone via AWDL. We demonstrate the data exchange via ICMPv6 echo request and replies as well as sending and receiving data over a TCP connection.
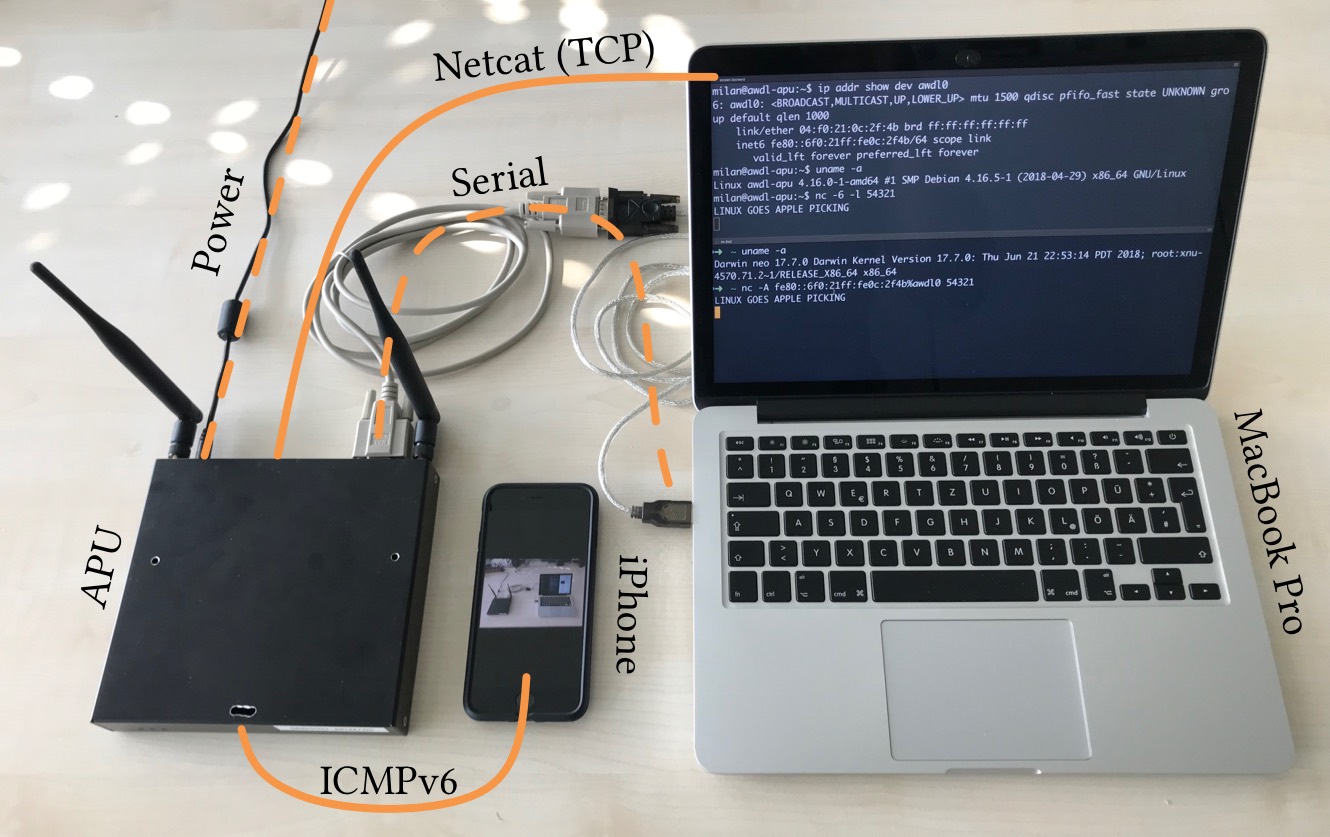
Demo Setup
Our demonstrator setup consists of a Linux-based APU board, an iPhone 8, and a MacBook Pro. The terminal on the MacBook’s screen shows a working TCP-over-AWDL connection between the APU board and the MacBook.